
February 25, 2024
Water, the very essence of life, deserves the utmost protection. Contamination from various sources threatens its purity, demanding effective filtration solutions.
Water filtration stands as a cornerstone of modern civilization, playing a vital role in ensuring access to clean, and safe drinking water for communities worldwide. Importance, methods, and cutting-edge technologies.
Tikal Water & Irrigation Systems rises to this challenge, offering a collection of powerful filtration methods and technologies proven to safeguard water quality across diverse applications. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of water filtration, exploring its process, usage, importance, methods, and cutting-edge technologies.
What is the Filtration Process?
Filtration is a physical process that removes impurities and contaminants from water by passing it through a porous medium. This medium, often made of sand, gravel, or activated carbon, acts as a barrier, trapping particles and bacteria while allowing clean water to pass through.
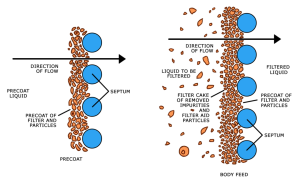
How Effectiveness Filtration Processes?
Statistics paint a concerning picture:
- 8 billion People globally lack access to safe drinking water (WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programmed).
- 80% of wastewater flows back into the environment untreated (UN Water).
Filtration plays a critical role in addressing these challenges by:

- Removing harmful contaminants: Bacteria, viruses, parasites, chemicals, and heavy metals are eliminated, ensuring water safety.
- Improving water quality: Clarity, taste, and odor are enhanced, making water more palatable and suitable for various uses.
- Protecting human health: Waterborne diseases are prevented, safeguarding public health and well-being.
- Preserving the environment: Wastewater treatment reduces pollution in rivers, lakes, and oceans, protecting ecosystems.
Filtration… Effective Process for multi Sectors
Water filtration finds widespread application across various sectors, including residential, commercial, industrial, and municipal settings. From purifying drinking water to treating wastewater and industrial effluents, filtration plays a critical role in safeguarding public health, protecting the environment, and supporting economic activities.

Water filtration methods and technologies are grounded in fundamental scientific principles that govern the behavior of particles, contaminants, and water molecules. Understanding these scientific foundations is essential for designing effective filtration systems. Here, we explore the scientific principles underlying various filtration methods and technologies:
Physical Filtration

Principle: Physical filtration relies on the size exclusion principle, where particles larger than the pore size of the filtration medium are unable to pass through.
Scientific Basis: This principle is based on the physical properties of particles, such as size, shape, and mass, and the interactions between particles and the filtration medium.
Gravity Filtration:
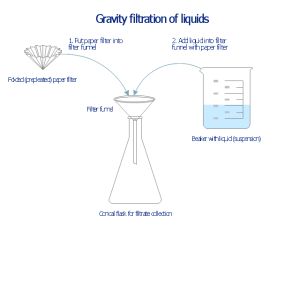
Principle: Gravity filtration utilizes gravitational force to drive water through a filtration medium, typically a porous material.
Scientific Basis: Gravity acts as the driving force, pulling water downward through the filter medium. The rate of filtration is influenced by factors such as the height of the water column and the porosity of the medium.
Pressure Filtration:
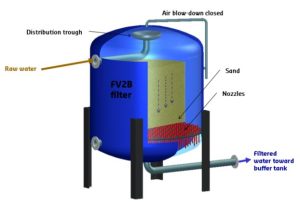
Principle: Pressure filtration applies mechanical pressure to force water through a filter medium, increasing the rate of filtration.
Scientific Basis: Pressure is applied to overcome the resistance of the filtration medium, enhancing the flow of water through the pores. This principle follows Darcy’s law, which describes the flow of fluids through porous media under pressure.
Membrane Filtration
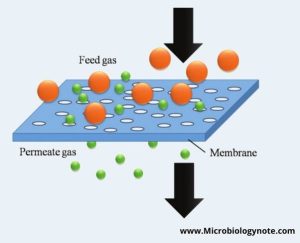
Principle: Membrane filtration uses semi-permeable membranes with precise pore sizes to separate particles and contaminants from water.
Scientific Basis: Membrane filtration is governed by principles of diffusion, osmosis, and sieving. Water molecules pass through the membrane pores, while larger particles and contaminants are retained based on size and charge.
Activated Carbon Filtration
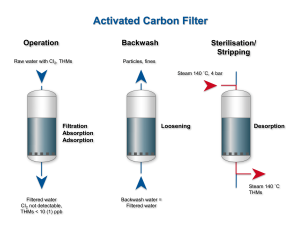
Principle: Activated carbon filtration relies on the adsorption of organic compounds, chemicals, and odors onto the surface of activated carbon particles.
Scientific Basis: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where molecules adhere to the surface of a solid material. Activated carbon has a large surface area and pore structure, allowing it to trap and remove contaminants from water through physical and chemical interactions.
Reverse Osmosis
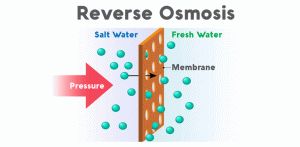
Principle: Reverse osmosis utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to remove dissolved solids, ions, and contaminants from water by applying pressure.
Scientific Basis: Reverse osmosis is based on the principles of osmosis and selective permeability. Pressure is applied to the feed water, forcing it through the membrane, while contaminants are rejected based on size and charge.
Tikal’s Filtration Arsenal: Tailored Solutions for Every Need:

Tikal understands all this fundamental scientific principles, So we go beyond a one-size-fits-all approach. We offer a diverse toolkit of filtration methods, each with specific strengths:
- Gravity filters: Simple and efficient, ideal for pre-treatment in large-scale applications.
- Rapid sand filters: High-flow capacity, effectively removing particles in municipal plants and industrial settings.
- M-Block rapid sand filters: Modular and easy to install, perfect for space-constrained locations.
- Prefiltration: Micro strainers and cartridge filters tackle larger particles before primary filtration.
- Membrane filtration: Reverse osmosis membranes remove dissolved contaminants, delivering exceptional water quality.
- Ion exchange systems: Target specific ions like hardness minerals for specialized needs.
